Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Image Preprocessing¶
This script illustrates the preprocess steps implemented prior to starting the pipeline of reconstructing a 3D map using simulated 2D images.
import os
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from aspire.noise import WhiteNoiseAdder
from aspire.operators import RadialCTFFilter
from aspire.source.simulation import Simulation
from aspire.volume import Volume
file_path = os.path.join(
os.path.dirname(os.getcwd()), "data", "clean70SRibosome_vol_65p.mrc"
)
Specify Parameters¶
# Set the initial simulated full size of images.
img_size = 33
# Set the demonstration downsampled image size.
ds_img_size = 15
# Set the total number of images generated from the 3D map
num_imgs = 512
# Set the noise variance and build the noise filter
noise_variance = 4e-1
noise_adder = WhiteNoiseAdder(var=noise_variance)
# Specify the CTF parameters not used for this example
# but necessary for initializing the simulation object
pixel_size = 5 * 65 / img_size # Pixel size of the images (in angstroms)
voltage = 200 # Voltage (in KV)
defocus_min = 1.5e4 # Minimum defocus value (in angstroms)
defocus_max = 2.5e4 # Maximum defocus value (in angstroms)
defocus_ct = 7 # Number of defocus groups
Cs = 2.0 # Spherical aberration
alpha = 0.1 # Amplitude contrast
Build Simulation Object and Apply Noise¶
print("Initialize simulation object and CTF filters.")
# Create CTF filters
ctf_filters = [
RadialCTFFilter(voltage, defocus=d, Cs=2.0, alpha=0.1)
for d in np.linspace(defocus_min, defocus_max, defocus_ct)
]
# Load the map file of a 70S ribosome and downsample the 3D map to desired image size.
print("Load 3D map from mrc file")
vols = Volume.load(file_path)
# Downsample the volume to a desired image size and increase density
# by 1.0e5 time for a better graph view
print(f"Downsample map to a image size of {img_size} x {img_size} x {img_size}")
vols = vols.downsample(img_size) * 1.0e5
# Create a simulation object with specified filters and the downsampled 3D map
print("Use downsampled map to create simulation object.")
source = Simulation(
L=img_size,
n=num_imgs,
vols=vols,
unique_filters=ctf_filters,
noise_adder=noise_adder,
pixel_size=pixel_size,
)
Initialize simulation object and CTF filters.
Load 3D map from mrc file
Downsample map to a image size of 33 x 33 x 33
Use downsampled map to create simulation object.
Apply Independent Preprocessing Techniques¶
Now we’ll apply each technique sequentially. This is easily
accomplished because each preprocessing technique returns a new
ImageSource object. In this case we assign each to a new
variable source_*. That leaves the original source object
untouched.
print("Obtain original images.")
imgs_od = source.images[0].asnumpy()
print("Perform phase flip to input images.")
source_pf = source.phase_flip()
print(f"Downsample image size to {ds_img_size} X {ds_img_size}")
source_ds = source.downsample(ds_img_size)
print("Normalize images to background noise.")
source_nb = source.normalize_background()
print("Whiten noise of images")
source_wt = source.whiten()
print("Invert the global density contrast if need")
source_rc = source.invert_contrast()
Obtain original images.
Perform phase flip to input images.
Downsample image size to 15 X 15
Normalize images to background noise.
Whiten noise of images
0%| | 0/1 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
100%|██████████| 1/1 [00:00<00:00, 1.61it/s]
100%|██████████| 1/1 [00:00<00:00, 1.60it/s]
Invert the global density contrast if need
0%| | 0/1 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
100%|██████████| 1/1 [00:00<00:00, 1.62it/s]
100%|██████████| 1/1 [00:00<00:00, 1.62it/s]
Plot First Image from Each Preprocess Step¶
Plot the first images.
print("Plot first image from each preprocess steps")
idm = 0
plt.subplot(2, 3, 1)
plt.imshow(imgs_od[idm], cmap="gray")
plt.colorbar(orientation="horizontal")
plt.title("original image")
plt.subplot(2, 3, 2)
plt.imshow(source_pf.images[0].asnumpy()[idm], cmap="gray")
plt.colorbar(orientation="horizontal")
plt.title("phase flip")
plt.subplot(2, 3, 3)
plt.imshow(source_ds.images[0].asnumpy()[idm], cmap="gray")
plt.colorbar(orientation="horizontal")
plt.title("downsample")
plt.subplot(2, 3, 4)
plt.imshow(source_nb.images[0].asnumpy()[idm], cmap="gray")
plt.colorbar(orientation="horizontal")
plt.title("normalize background")
plt.subplot(2, 3, 5)
plt.imshow(source_wt.images[0].asnumpy()[idm], cmap="gray")
plt.colorbar(orientation="horizontal")
plt.title("noise whitening")
plt.subplot(2, 3, 6)
plt.imshow(source_rc.images[0].asnumpy()[idm], cmap="gray")
plt.colorbar(orientation="horizontal")
plt.title("invert contrast")
plt.tight_layout()
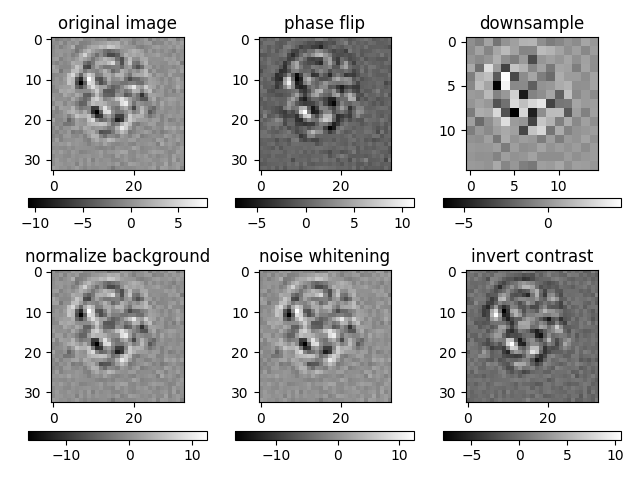
Plot first image from each preprocess steps
Apply Sequential Preprocessing Techniques¶
Now we’ll apply each technique sequentially.
This is accomplished by reassigning each new ImageSource to the same variable.
In this case we reassign to source.
Note, after each source assignment we’ll manually save off the images for the plot below.
# We'll copy ``source`` so we can use it in a later section.
# Since ``source`` objects are designed to follow an immutable usage by default (like Numpy arrays),
# we can copy a source just by copying the object.
source_copy = source
print("Obtain original images.")
imgs_seq_od = source.images[0].asnumpy()
print("Perform phase flip to input images.")
source = source.phase_flip()
imgs_seq_pf = source.images[0].asnumpy()
print(f"Downsample image size to {ds_img_size} X {ds_img_size}")
source = source.downsample(ds_img_size)
imgs_seq_ds = source.images[0].asnumpy()
print("Normalize images to background noise.")
source = source.normalize_background()
imgs_seq_nb = source.images[0].asnumpy()
print("Whiten noise of images")
source = source.whiten()
imgs_seq_wt = source.images[0].asnumpy()
print("Invert the global density contrast if need")
source = source.invert_contrast()
imgs_seq_rc = source.images[0].asnumpy()
Obtain original images.
Perform phase flip to input images.
Downsample image size to 15 X 15
Normalize images to background noise.
Whiten noise of images
0%| | 0/1 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
100%|██████████| 1/1 [00:00<00:00, 1.50it/s]
100%|██████████| 1/1 [00:00<00:00, 1.49it/s]
Invert the global density contrast if need
0%| | 0/1 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
100%|██████████| 1/1 [00:00<00:00, 1.43it/s]
100%|██████████| 1/1 [00:00<00:00, 1.43it/s]
Plot First Image from Each Preprocess Step¶
Plot the first images.
print("Plot first image from each preprocess steps")
idm = 0
plt.subplot(2, 3, 1)
plt.imshow(imgs_od[idm], cmap="gray")
plt.colorbar(orientation="horizontal")
plt.title("original image")
plt.subplot(2, 3, 2)
plt.imshow(imgs_seq_pf[idm], cmap="gray")
plt.colorbar(orientation="horizontal")
plt.title("phase flip")
plt.subplot(2, 3, 3)
plt.imshow(imgs_seq_ds[idm], cmap="gray")
plt.colorbar(orientation="horizontal")
plt.title("downsample")
plt.subplot(2, 3, 4)
plt.imshow(imgs_seq_nb[idm], cmap="gray")
plt.colorbar(orientation="horizontal")
plt.title("normalize background")
plt.subplot(2, 3, 5)
plt.imshow(imgs_seq_wt[idm], cmap="gray")
plt.colorbar(orientation="horizontal")
plt.title("noise whitening")
plt.subplot(2, 3, 6)
plt.imshow(imgs_seq_rc[idm], cmap="gray")
plt.colorbar(orientation="horizontal")
plt.title("invert contrast")
plt.tight_layout()
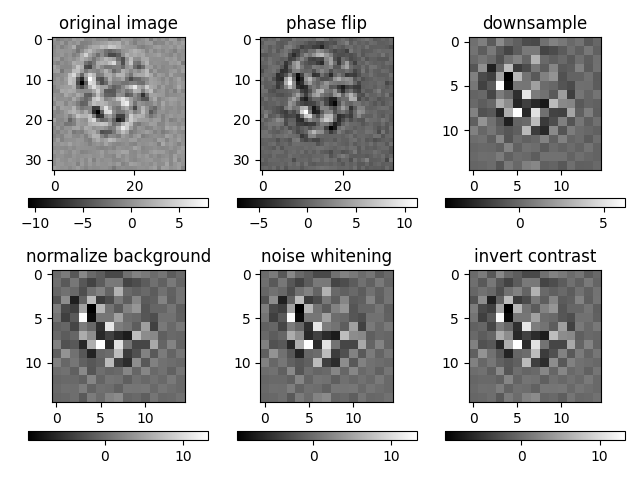
Plot first image from each preprocess steps
Apply Chained Preprocessing Techniques¶
Now we’ll apply the preprocessing in a chain syntax
# We'll reset our ``source`` to the reference copy we started with.
source = source_copy
print("Perform phase flip to input images.")
print(f"Downsample image size to {ds_img_size} X {ds_img_size}")
print("Normalize images to background noise.")
print("Whiten noise of images")
print("Invert the global density contrast if need")
source = (
source.phase_flip()
.downsample(ds_img_size)
.normalize_background()
.whiten()
.invert_contrast()
)
# Assign the first image from the preprocessed chain.
imgs_chained = source.images[0].asnumpy()
# This preprocessing chain should correspond to applying each
# operation sequentially.
assert np.allclose(imgs_chained, imgs_seq_rc)
Perform phase flip to input images.
Downsample image size to 15 X 15
Normalize images to background noise.
Whiten noise of images
Invert the global density contrast if need
0%| | 0/1 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
100%|██████████| 1/1 [00:00<00:00, 1.55it/s]
100%|██████████| 1/1 [00:00<00:00, 1.55it/s]
0%| | 0/1 [00:00<?, ?it/s]
100%|██████████| 1/1 [00:00<00:00, 1.40it/s]
100%|██████████| 1/1 [00:00<00:00, 1.40it/s]
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 5.167 seconds)